class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
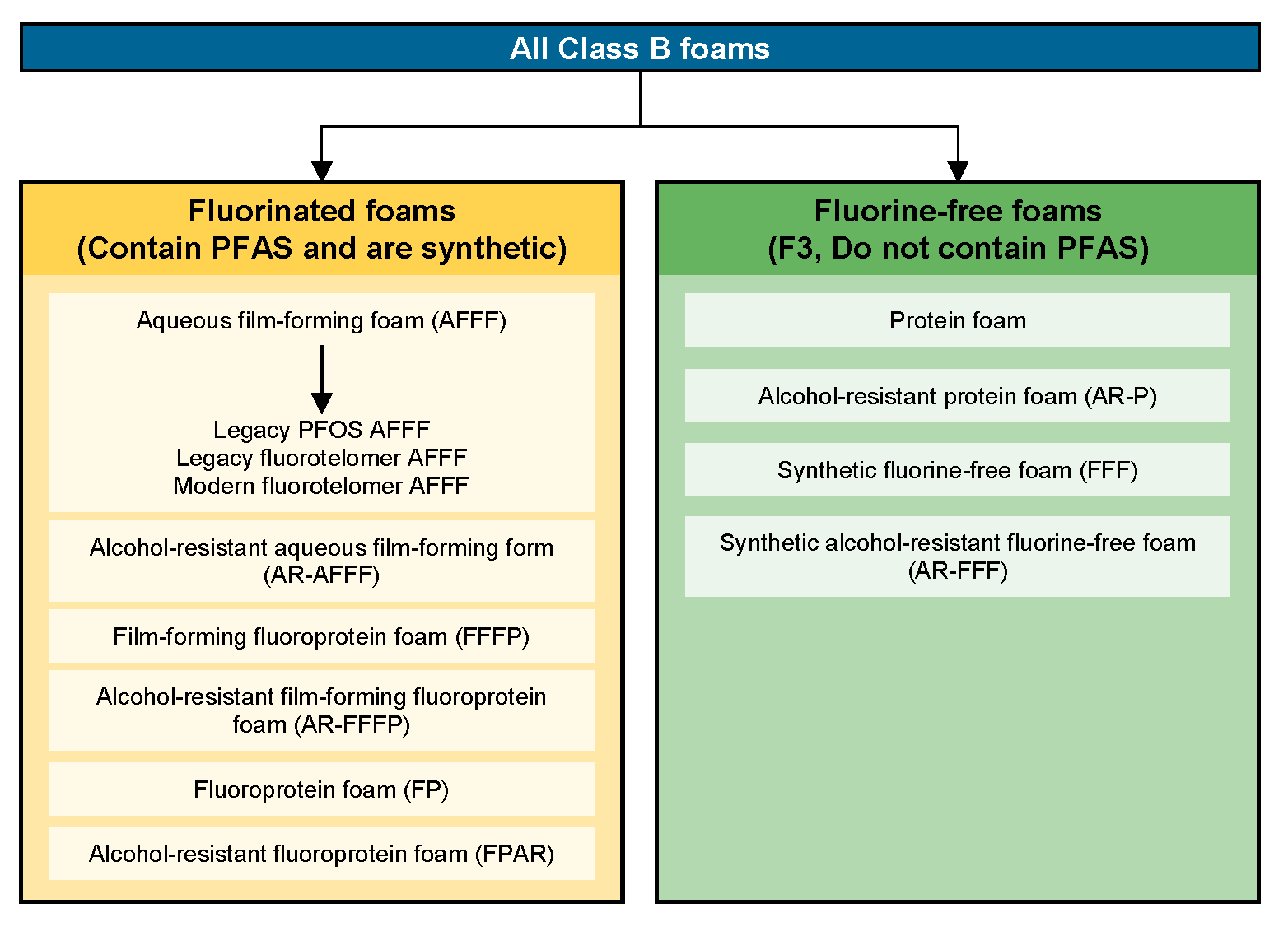
Assume a fairly short period of time up to about 15 to 30 minutes of effectiveness in normal wildland conditions. This law prohibits the use of Class B and Class AB firefighting foams that contain intentionally added per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances PFAS except in the following two situations.

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
Anionic surfactants are the initial and most developed and the leading class in several forms of surfactants.
. In most foams the volume of gas is large with thin films of liquid or solid separating the regions of gas. When used as a wetting agent the concentrate lowers the surface tension of the water allowing better penetration into deep seated fires. The fluorinated surfactants used in AFFF are produced by one of two synthetic processes 1.
A bath sponge and the head on a glass of beer are examples of foams. When used as part of an emergency firefighting or fire. In general anionic surfactants tend to generate higher foam levels than other classes of surfactants.
The term surfactant comes from the words surface active agent. Solid foams can be closed-cell or open-cell. Wetting and emulsifying TERGITOL Surfactants deliver low foam excellent solvency chemical stability and reliable formulation performance in a number of fermentation food processing.
Water Foam Class A concentrate is simply a surfactant similar to dishwashing soap that reduces surface tension. CLASS A FOAM CONCENTRATE. They are added to remove dirt from skin clothes and household articles particularly in kitchens and bathrooms.
Class A foams may be used as a firefighting agent or as a fire barrier. A foam concentrate containing fluorochemical surfactants that control the physical properties of water enabling it to float and spread across the surface of the hydrocarbon liquid. The rate of application for class B foam depends on what five factors.
Class A foam is primarily a surfactant which is to say that it breaks down the surface tension of water. Costs of equipment Departments reported equipment costs up to 5000 per unit for nozzle-aspirated class A foam systems. Foam is an object formed by trapping pockets of gas in a liquid or solid.
They may be broadly employed as foaming agents antistatic agents dispersants detergents emulsifiers and stabilizers in the biochemical features of life 29. One class of fluorosurfactants used in AFFF formulations is based on perfluorooctyl sulfonate PFOS and structurally related compounds. The second reason that surfactants help create foam is that the liquid in the foam walls is naturally sucked out of the walls into the edges.
2019 Wisconsin Act 101 was published on Feb. CAFS units may cost up to 40000 per vehicle. This is a biodegradable mixture of foaming and wetting agents.
Dow produces surfactants that act as emulsifiers dispersants wetting agents for crop. Costs for training Most departments did not quantify the cost of training their personnel to operate class A foam systems. These are prepared by direct electrochemical fluorination.
When added to water the resulting foam solution consists of many smaller droplets with much more surface area allowing faster heat absorption. An example would be like cooling a glass of water with a single ice cube. In addition the portion of the foam concentrate molecule that repels other water in order.
Denkov et al Role of surfactant type and bubble surface mobility in foam rheology Soft Matter 5 2009 3389 review. Surfactants are one of many different compounds that make up a detergent. 6 2020 and codified in s.
They are also used extensively in industry. AFFF Aqueous Film Forming Foam. This is a biodegradable mixture of foaming and wetting agents.
When mixed in correct proportions with water it can change two properties of the water. Tcholakova et al Role of surfactant type and concentration for the mean drop size during emulsification in. 2 Whether the fuel is on fire.
Figure 1 Surfactants aid the effective. In particular AFFF manufactured by the 3M Corporation sold prior to. Difference was noted with nozzle-aspirated class A foam.
The energy need to increase the surface area A is γδAδt so a low γ means more foam for less energy. As foam generation and also foam stability is a dynamic for process for generating and reducing surface area in a surfactantwater system the diffusion of the surfactant to the surface and the change in surface coverage at least locally during bubble generation and drainage of the film is a more useful way of explaining foam properties. 5 foam application via fisxed system or portable equipment.
Act 101 2019 Wisconsin Act 101. Global supply from world-class manufacturing facilities. Anionic surfactants are effective in removing particulate soils 11.
Soap foams are also known as suds. When mixed in correct proportions with water it can change two properties of the water. Class A foam will increase wetting effectiveness.
1 Type of foam concentrate used. So a surfactant which reaches the lowest surface tension for the least amount of surfactant is in general going to give an easier longer-lasting foam. Class B foam is used on flammable liquids.
Nonionic surfactants are particularly efficient at removing oily soils from synthetic fabrics but they are not as efficient at removing particulate soils as anionic surfactants. Aqueous film forming foam AFFF means a fluorinated surfactant with a foam stabilizer which is diluted with water to act as a temporary barrier to exclude air from mixing with the fuel vapor by developing an aqueous film on the fuel surface of some hydrocarbons which is capable of suppressing the generation of fuel vapors. In closed-cell foam the gas forms discrete.
The pressure inside a foam of radius R that contributes to its self-destruction is 2γR. PFOA and PFOS form a class of chemicals called perfluorinated compounds PFCs that act as surfactants to improve the effectiveness of Class B firefighting foams in fighting petroleum and other fires. This is nothing to do with drainage as explained in Drainage the walls contain an irrelevant.
Class A Foams are approved for application from ground equipment and helicopter buckets. Class A foam is used on common combustibles such as paper wood and textiles. As a fire barrier Class A foams increase moisture con-tent in Class A combustibles preventing the ignition of these type fuels.
Some products also are approved for application from singleengine airtankers SEATs andor - fixed-tank helicopters. 3 type of feul hydrocarbonpolar solvent 4 whether fuel is spilled or contained in tank.

Phos Chek Wd881 Class A Foam 5 Gallon Pail Linegear

Stability Of Foam An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
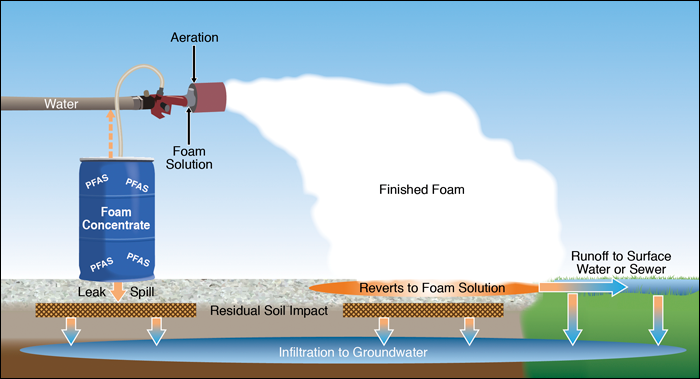
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Surface Active Agents Surfactants Types And Applications

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
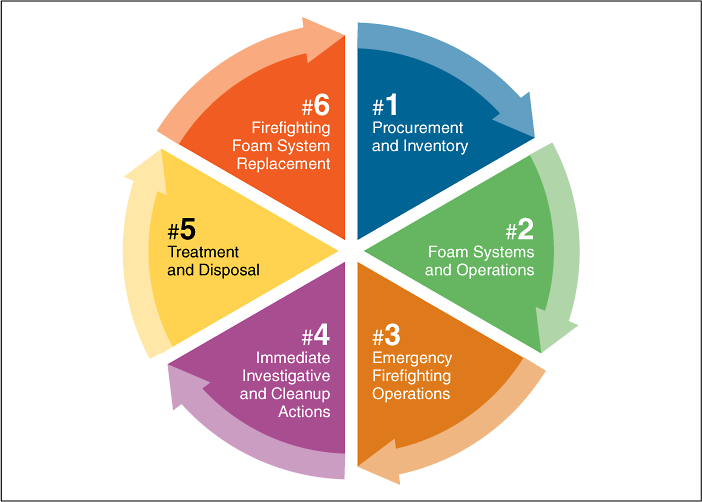
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

What Are Surfactants Surfactants Meaning Types Of Surfactants Surfactant Examples Anionic Surfactants

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex
Foam Making Practical Surfactants Science Prof Steven Abbott

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Despite Advantages Of Using Class A Foam To Battle Wildfires Use Is Down That Needs To Change International Fire Fighter

Types Of Firefighting Foam Vanguard Fire And Security

How Does A Fire Fighting Foam Concentrate Work On Fire Bioex

Compatibility Of Aqueous Film Forming Foams Afff With Sea Water Sciencedirect
![]()
Class A Foam Is The Best Tool For Fighting Fires So Why Aren T Fire Departments Using It Claimsmate

Phos Chek Wd881 Class A Foam Fire Product Search

3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances